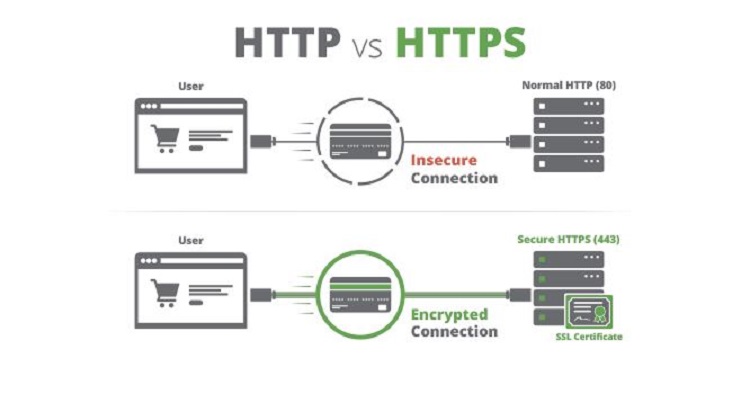
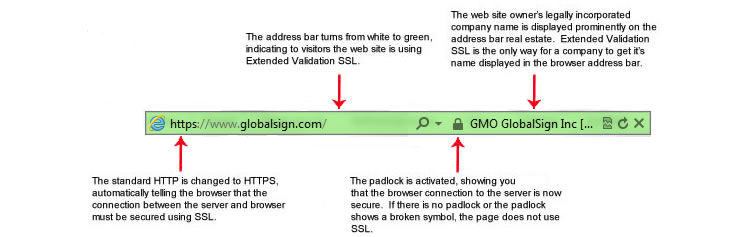
What is a security policy?
A security policy is a formal, detailed and easily understandable document that addresses general beliefs, goals, acceptable procedures and security controls that governs an organization or other entity. It addresses the constraints on behavior of its members as well as constraints imposed on adversaries by mechanisms such as doors, locks, keys and walls, computer security threats, and how to handle situations when they do occur. A security policy must identify all of a company’s assets as well as all the potential threats to those assets. And lastly, it should be subject to amendment as threats have a dynamic.
Why a security policy?
A security policy should be one of the first documents in place for a corporate organization or entity to function flexibly. It should address all security concerns, the likelihood that they will actually occur, ways forward and speculation clearly so that the employees and employers feel at ease implementing their mandate. So you need a security policy so as to:
- Establish the rules for user behavior on use of organizational assets. This ensures proper compliance of the staff.
- To define and authorize consequences of violation of certain guidelines.
- Establish baseline stance on security to minimize the risk of occurrences in the organization.
- Builds a sense of carefulness among staff therefore reduces risk of data loss or leak.
- Protects the organization from external and internal “malicious” users.
- Guides staff on acceptable and unacceptable behavior.
- Carries with itself how information is disseminated (private, internal & public information).
A Good Security Policy
A good security policy should be readily available for its intended audience. It shouldn’t be hard to get.
It should be understandable and not confusing. Avoid using words that are beyond the understanding of your audience. It should clearly indicate how violations are handled.
A security policy should be applicable to the organization and only reveal information relevant to the functionality of the organization. It should cover use of organization assets, specify minimum security standards used in protection of assets, prohibitions against malicious actions, home use of organization equipment, use of personal equipment for carrying out official duties, procedures deemed as accepted or best practices, etc.
Work to develop a policy that balances both current practices of the organization and practices the organization wants to see in future. And most importantly make sure to have a policy that protects and organization against multiple types of threats.
And lastly, It should be accepted, put into use and reviewed frequently, at least once a year upcoming concerns should be updated in it. This is because breaches will always keep evolving and therefore new measures have to come in place.
5 steps to compile a good security policy
- Identify issues
- Conduct a context analysis on issues identified. (vulnerabilities, fix/ways forward, influence of behavior). Set of rules
- Make a draft policy covering all the above.
- Have a review of the document internally and or hire an external entity to review too.
- Deploy the policy to the rest of the organization.
Document Outline
- Introduction
- Purpose
- Scope
- Roles and responsibilities
- Sanctions and violations
- Review schedule
- Definition of terms, abbreviations/acronyms
Topics should center around the following
- Physical Security
- Security Training
- Privacy
- Software Licencing
- Password
- Virus protection
- Acceptable use
- Account management
- Special access (Authority)
- Change management
- Incident management